What Is a Portable Oxygen Concentrator?
A portable oxygen concentrator (POC) is a compact, lightweight medical device designed to deliver supplemental oxygen to individuals experiencing low blood oxygen levels. This FDA-approved device continuously extracts and purifies oxygen from the surrounding air, eliminating the need for refills or replacements.
The primary purpose of a POC medical device is to support patients with respiratory conditions by maintaining adequate oxygen saturation throughout their daily activities. Unlike stationary concentrators or bulky oxygen tanks, these devices offer genuine mobility without compromising therapeutic effectiveness.
Key characteristics that define a POC:
- Portability: Weighs between 2-10 pounds depending on the model, making it easy to carry
- Self-sufficient operation: Generates oxygen on-demand from ambient air rather than storing compressed gas
- Battery-powered capability: Enables use during travel, outdoor activities, and away from power sources
- Compact design: Small enough to fit in a backpack or shoulder bag
Traditional oxygen tanks can weigh upwards of 50 pounds when full and require regular refilling from medical suppliers. A portable oxygen concentrator definition centres on its ability to provide continuous oxygen therapy whilst allowing users to maintain an active lifestyle. The device transforms atmospheric air into concentrated oxygen, delivering it directly to the user through a nasal cannula or mask according to their prescribed flow rate.
How Does a Portable Oxygen Concentrator Work?
A portable oxygen concentrator transforms regular air into concentrated oxygen through a sophisticated four-stage process. The device draws in atmospheric air—which naturally contains approximately 20% oxygen and 80% nitrogen—through an intake filter that removes dust and particles.
1. Air Intake
The process begins with the device drawing in air from the environment. This air contains both oxygen and nitrogen.
2. Air Compression
An internal air compressor then pressurises the filtered air. This compression step is essential for preparing the air to move through the device’s filtration system efficiently.
3. Filtration with Zeolite Sieve Beds
The pressurised air enters the sieve beds, which are made of a material called zeolite. These sieve beds are designed to separate oxygen from nitrogen.
As compressed air flows through these beds, the zeolite material acts like a molecular sieve, trapping nitrogen molecules whilst allowing smaller oxygen molecules to pass through freely. This selective filtration happens rapidly, with the device alternating between two sieve beds—one filtering whilst the other releases trapped nitrogen back into the atmosphere.
4. Oxygen Collection
The result is medical-grade oxygen with 90-95% purity, significantly higher than the 20% found in ambient air. This concentrated oxygen collects in a small internal reservoir, ready for delivery to the user.
The entire cycle repeats continuously, ensuring a steady supply of purified oxygen without requiring refills or external oxygen sources.
How Is Oxygen Delivered to the User Through a Portable Oxygen Concentrator?
Once purified, the concentrated oxygen collects in a small internal reservoir within the device, ready for immediate delivery. The device channels this oxygen through flexible tubing connected to either a nasal cannula (small prongs that fit into the nostrils) or a face mask, depending on the user’s prescription and comfort preferences.
Oxygen delivery methods come in two distinct forms:
1. Pulse Dose Mode
This mode releases oxygen only when the device detects inhalation. A built-in sensor monitors breathing patterns and triggers oxygen delivery precisely when the user breathes in. This intelligent system conserves oxygen and extends battery life, making it ideal for:
- Active daytime use
- Walking and light exercise
- Travel and outdoor activities
- Users with stable oxygen needs
2. Continuous Flow Mode
This mode provides a steady, uninterrupted stream of oxygen regardless of breathing patterns. The device maintains constant oxygen output at prescribed flow rates measured in litres per minute (LPM). This mode suits:
- Nighttime use during sleep
- Patients with severe respiratory conditions
- Situations requiring consistent oxygen saturation
- Medical protocols demanding continuous supplementation
Most modern portable concentrators offer both modes, though some lightweight models focus exclusively on pulse dose delivery to maximise portability. Healthcare providers determine which delivery method matches individual oxygen requirements based on activity levels, severity of respiratory condition, and blood oxygen measurements.
What Powers Portable Oxygen Concentrators?
Portable oxygen concentrators (POCs) operate using two primary power sources: electrical outlets and rechargeable batteries. When at home or in a stationary location, users can plug their device directly into a standard wall socket for unlimited operation. The battery option transforms these devices into truly mobile solutions, allowing users to maintain their oxygen therapy whilst travelling, shopping, or participating in outdoor activities without being tethered to a power source.
For more detailed insights into the operation and benefits of portable oxygen concentrators, you can refer to this comprehensive guide on portable oxygen concentrators.
Battery Life and Performance
Battery life portable concentrator performance varies significantly based on several factors. Most devices offer between 2 to 10 hours of battery operation, depending on the model, flow settings, and whether the unit operates in pulse dose or continuous flow mode. Higher flow settings and continuous delivery modes consume more power, reducing operational time. Many manufacturers offer extended battery packs that can double or triple usage time between charges.
Benefits of Electrical Outlet Power
The electrical outlet power option ensures uninterrupted therapy during extended periods at home or in vehicles equipped with DC power adapters. Modern POCs often include car chargers, enabling users to recharge whilst driving to appointments or on road trips.
Advantages of Battery Operation
Battery operation delivers exceptional mobility benefits that fundamentally change users’ quality of life. Patients can attend social gatherings, visit family members, and maintain independence without worrying about running out of oxygen mid-activity. This freedom represents a stark contrast to traditional oxygen tanks, which offer limited capacity and require careful planning around refill schedules.
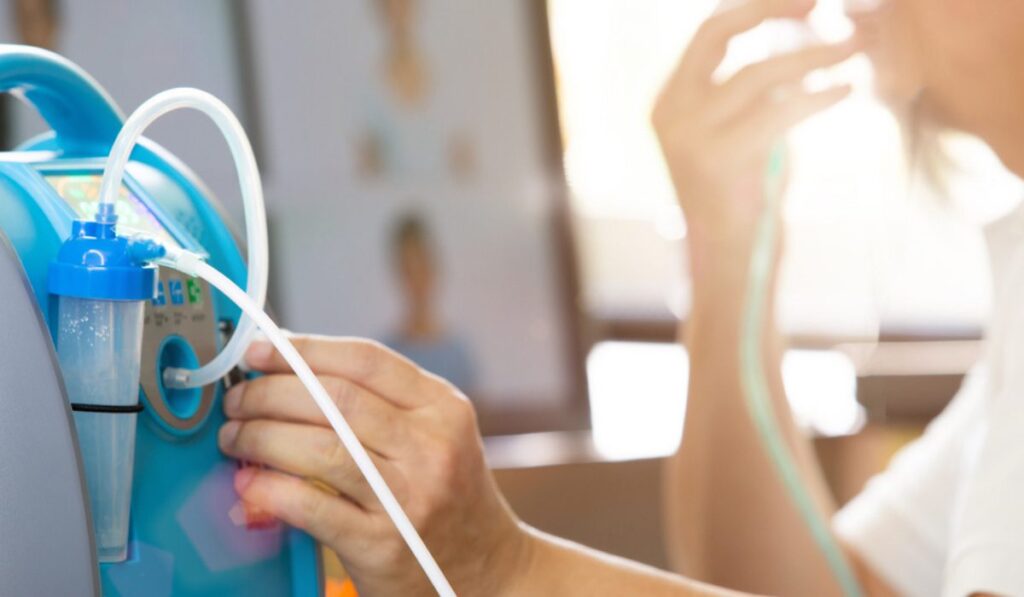

Why Are Portable Oxygen Concentrators Beneficial Compared to Traditional Oxygen Tanks?
The advantages of portable oxygen concentrators over traditional oxygen tanks centre on independence, safety, and convenience. Traditional oxygen tanks store compressed gas that depletes with use, requiring regular refills or complete cylinder replacements—a process that demands scheduling, delivery coordination, and constant monitoring of remaining oxygen levels.
POCs eliminate this burden entirely. These devices generate oxygen continuously from ambient air, meaning users never face the anxiety of running out mid-activity or the logistical challenges of arranging emergency refills. The technology transforms how patients manage their oxygen therapy, shifting from a supply-dependent model to an on-demand generation system.
Safety represents another critical distinction in the POC vs traditional tanks comparison. Compressed oxygen cylinders pose inherent risks:
- Potential explosion hazards if mishandled or exposed to heat
- Fire acceleration properties of concentrated oxygen under pressure
- Physical dangers from heavy cylinders tipping or falling
- Strict transportation regulations limiting where tanks can travel
Portable oxygen concentrators contain no pressurised gas, significantly reducing these safety concerns. The devices simply process ambient air, making them safer for home use and travel.
Mobility with portable oxygen transforms daily life. Weighing between 2-7 kilograms depending on the model, POCs accompany users on aeroplanes (most models are FAA-approved), in cars, through shopping centres, and during social activities. Traditional tanks, weighing 20-50 kilograms when full, severely restrict movement and often confine users to their homes. Battery-powered operation means POC users maintain active lifestyles without proximity to oxygen supply companies.
Who Typically Uses Portable Oxygen Concentrators?
POC users primarily include individuals diagnosed with chronic respiratory conditions that compromise their body’s ability to maintain healthy blood oxygen levels. Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) represent the largest group requiring COPD oxygen therapy, as this progressive lung disease significantly reduces oxygen absorption capacity.
Beyond COPD, portable oxygen concentrators serve patients managing:
- Pulmonary fibrosis – scarring of lung tissue that impairs oxygen transfer
- Severe asthma – when attacks or chronic inflammation restricts airflow
- Cystic fibrosis – genetic condition affecting lung function
- Pneumonia – during recovery when oxygen levels remain low
- Heart failure – when the heart cannot pump sufficient oxygenated blood
Maintaining adequate oxygen saturation proves critical for these individuals. Low blood oxygen levels (hypoxemia) can cause fatigue, confusion, shortness of breath, and long-term organ damage. Consistent oxygen supplementation helps preserve cognitive function, physical stamina, and prevents complications.
Portable oxygen concentrators are FDA-approved medical devices available only through prescription. Healthcare providers conduct thorough assessments including pulse oximetry readings and arterial blood gas tests to determine each patient’s specific oxygen requirements. The prescription specifies flow rate settings, delivery mode (pulse or continuous), and duration of use – ensuring the device meets individualised therapeutic needs rather than a one-size-fits-all approach.
In recent years, advancements in medical technology have greatly improved the efficacy and accessibility of such devices. For instance, Roche, a leading healthcare company, has been making strides in developing innovative solutions that enhance patient care and treatment outcomes.
See Also : How Long Does a Portable Oxygen Cylinder Last on One Charge?
How Can Users Maintain and Care for Their Portable Oxygen Concentrators?
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of your portable oxygen concentrator and ensures it delivers oxygen at prescribed levels. Cleaning air filters weekly stands as the most critical maintenance task, as clogged filters reduce airflow and force the device to work harder, potentially causing overheating or component failure.
Most POC models feature washable external filters that require gentle cleaning with mild soap and warm water. After washing, allow filters to air dry completely before reinstalling them—typically 24 hours. Some devices also contain internal filters that need professional servicing or replacement at intervals specified in your user manual.
Following Manufacturer Instructions for Optimal Device Longevity and Performance
Each POC model has unique maintenance requirements detailed in its manufacturer instructions. These guidelines specify:
- Filter replacement schedules (ranging from monthly to annually depending on usage)
- Approved cleaning solutions that won’t damage sensitive components
- Battery care protocols including proper charging cycles and storage temperatures
- Service intervals for professional inspection and calibration
Proper handling practices protect your device from damage. Store your concentrator in a cool, dry location away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Avoid placing the unit on soft surfaces like beds or sofas that can block air vents. When transporting your POC, use the manufacturer-provided carrying case to shield it from impacts and moisture.
Battery maintenance directly affects device reliability. Charge batteries according to manufacturer specifications, avoiding complete discharge when possible. Store spare batteries at room temperature in a dry environment. Most lithium-ion batteries in POCs maintain optimal performance when kept between 40-80% charge during extended storage periods.
Inspect tubing and cannulas regularly for cracks, kinks, or blockages. Replace these accessories every two weeks or as recommended, since worn tubing can leak oxygen and reduce therapy effectiveness. Keep the device’s exterior clean by wiping it with a damp cloth, avoiding harsh chemicals that might damage the casing or controls.
Conclusion
What Is a Portable Oxygen Concentrator and How Does It Work? The answer lies in sophisticated technology that transforms ambient air into life-sustaining therapy. POCs represent a revolutionary shift in respiratory care, merging advanced engineering with user-centred design to deliver consistent oxygen therapy without the limitations of traditional systems.
The importance of portable oxygen concentrators in modern therapy solutions extends beyond mere functionality. These devices eliminate the anxiety of running out of oxygen, the hassle of coordinating tank deliveries, and the physical strain of managing heavy equipment. Users gain freedom to maintain active lifestyles, travel confidently, and manage their respiratory conditions with dignity.
Ready to explore whether a portable oxygen concentrator is right for you? Consult with your healthcare provider to discuss your specific oxygen requirements and receive a proper prescription. The right POC can transform daily oxygen therapy from a burden into a seamless part of your routine, supporting your independence and wellbeing every step of the way.
FAQs about Portable Oxygen Concentrators (POCs)
A POC is a compact, lightweight medical device that extracts and delivers concentrated oxygen from ambient air for individuals with low blood oxygen levels.
2. How does a portable oxygen concentrator work?
It draws in air, compresses it, filters nitrogen through zeolite sieve beds, and delivers 90–95% pure oxygen to the user via a nasal cannula or mask.
3. What are the oxygen delivery modes in a POC?
POCs offer pulse dose mode (oxygen released during inhalation) and continuous flow mode (steady oxygen stream).
4. How are POCs powered?
They use rechargeable batteries for mobility and electrical outlets for home or stationary use.
5. How long does a POC battery last?
Battery life varies by model, flow rate, and mode, typically ranging 2–10 hours, with extended battery options available.
6. Why choose a portable oxygen concentrator over traditional oxygen tanks?
POCs offer mobility, independence, safety, and convenience, eliminating the need for heavy tanks and frequent refills.
7. Who typically uses a portable oxygen concentrator?
Patients with COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, severe asthma, cystic fibrosis, pneumonia, or heart failure often use POCs to maintain oxygen levels.
8. How should users maintain their portable oxygen concentrator?
Regularly clean air filters, inspect tubing, follow manufacturer instructions, and charge batteries properly to ensure optimal performance.
9. Are portable oxygen concentrators FDA-approved and prescription-only?
Yes. POCs are FDA-approved medical devices and require a prescription to ensure correct oxygen flow settings and safe use.


